What is Percutaneous Neuromodulation?
It consists of inserting a needle near an affected nerve or muscle, through which a low-frequency electrical current is applied, controlled by a device.
Percutaneous neuromodulation helps reduce pain and improve neuromuscular communication, promoting functional recovery and wellbeing.
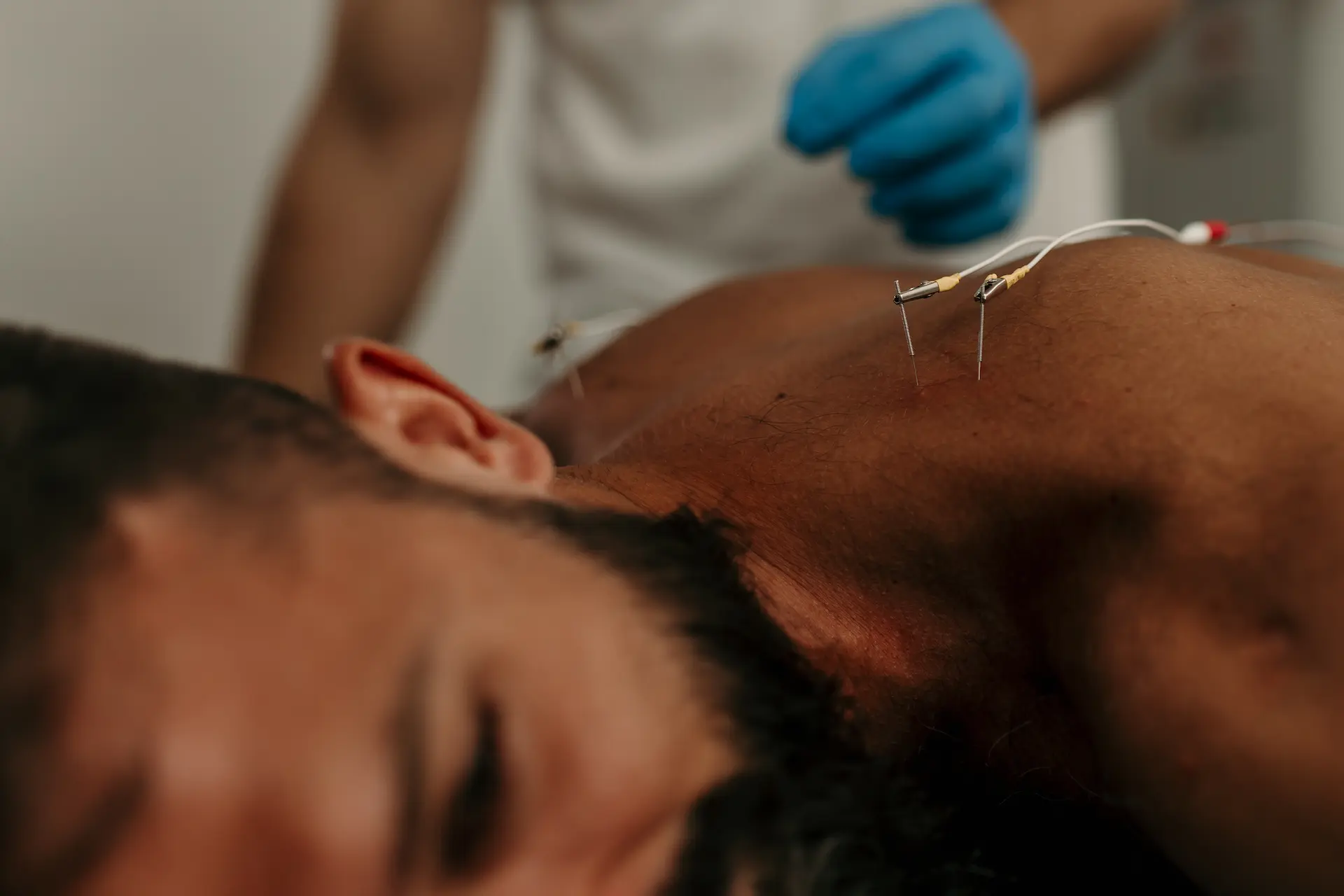
The goal is to stimulate the peripheral or central nervous system to improve neuromuscular communication, reduce pain, normalize muscle electrical activity, and promote functional recovery.
When can I benefit from Percutaneous Neuromodulation?
Percutaneous neuromodulation is used in a wide variety of musculoskeletal and neurological conditions, including:
Chronic or acute pain – of muscular, articular, or neuropathic origin.
Myofascial pain syndrome – relief of trigger points and muscle contractures.
Tendinopathies and sports injuries – treatment of overloads and functional improvement.
Radiculopathies or neuralgias – e.g., sciatic or pudendal nerve.
Paresis or muscle weakness – after nerve injuries or surgical interventions.
Are there any contraindications?
This procedure is contraindicated in patients with pacemakers or implanted defibrillators. In metal allergies, especially to nickel, standard acupuncture needles cannot be used. Pregnancy is not a contraindication, but if you are pregnant, you should inform us. Patients on anticoagulants are more prone to bleeding, as are immunocompromised or lymphadenectomized patients to infections. In hypothyroidism, edema may occur in the punctured muscle, and needling should be avoided in skin conditions such as psoriasis.
Are there any side effects?
The use of needles in percutaneous electrical stimulation can cause effects similar to other needling techniques. These include: local or nearby discomfort that disappears over time, dizziness in sensitive individuals, though without serious risk, infrequent side effects such as dermatitis, bruising, spasms, myoedema or infections (it is recommended to wait 24 hours before swimming), and possible “cramp” sensation when puncturing near a nerve...
Additionally, electrical stimulation may cause mild skin irritation and mild pain in the treated area or along the nerve path.


